How a Podiatrist Can Help With Ingrown Toenails
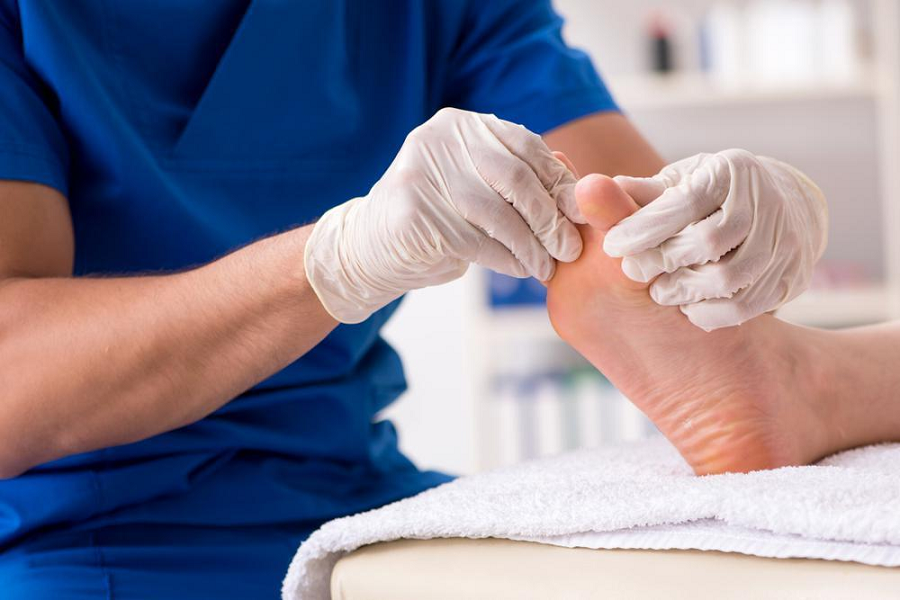
Podiatrists play a crucial role in diagnosing and treating various foot and ankle conditions, including ingrown toenails. An ingrown toenail occurs when the edge of the toenail grows into the surrounding skin, causing pain, swelling, and potential infection. Podiatrists are specially trained to address this common problem, providing both conservative and surgical interventions to alleviate discomfort and promote healing.
Here’s a comprehensive overview of how a podiatrist can help with ingrown toenails:
1. Diagnosis:
Clinical Examination:
A podiatrist will begin by conducting a thorough examination of the affected toe. They will assess the extent of ingrowth, inflammation, and potential signs of infection.
Medical History:
Understanding the patient’s medical history is crucial, as certain conditions, such as diabetes, can complicate the management of ingrown toenails.
2. Conservative Treatment:
Soaking the Feet:
In mild cases, podiatrists may recommend soaking the foot in warm water to help reduce inflammation and soften the skin around the ingrown toenail.
Topical Antibiotics:
If there are signs of infection, the podiatrist may prescribe or recommend topical antibiotics to prevent further complications.
Proper Nail Trimming:
Podiatrists educate patients on proper nail-cutting techniques to prevent recurrence. This includes cutting nails straight across and avoiding rounded edges.
3. Pain Management:
Pain Medication:
Over-the-counter pain medications may be recommended to manage pain and discomfort associated with ingrown toenails.
Topical Anesthetics:
In some cases, podiatrists may use topical anesthetics to numb the affected area before performing a procedure.
4. Surgical Intervention:
Partial Nail Avulsion (PNA):
If conservative measures fail or the ingrown toenail is recurrent, a podiatrist may opt for a partial nail avulsion. This involves removing a portion of the toenail, including the ingrown edge. This is a common and effective outpatient procedure performed in the podiatrist’s office.
Matrixectomy:
In severe or recurrent cases, the podiatrist may perform a matrixectomy, where a portion of the nail matrix is removed to prevent the ingrown toenail from returning.
5. Post-Procedure Care:
Dressing and Bandaging:
After any surgical procedure, the podiatrist will dress and bandage the affected toe appropriately. Patients are provided with instructions on how to care for the wound at home.
Follow-Up:
Regular follow-up appointments are scheduled to monitor the healing process and address any concerns.
6. Preventive Measures:
Footwear Recommendations:
Podiatrists may provide guidance on appropriate footwear to reduce pressure on the toes and prevent ingrown toenails.
Education:
Patients receive education on proper foot hygiene, nail care, and lifestyle changes to minimize the risk of ingrown toenails.
7. Management of Complications:
Infection Control:
If an infection is present, the podiatrist will take appropriate measures to control and treat it, which may include prescription antibiotics.
Wound Care:
Podiatrists are trained to manage post-operative complications and ensure proper wound healing.
8. Patient Education:
Lifestyle Modifications:
Podiatrists educate patients on lifestyle changes that can prevent the recurrence of ingrown toenails, such as maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding tight or ill-fitting shoes.
In conclusion, podiatrists play a vital role in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of ingrown toenails. Their expertise in both conservative and surgical interventions ensures that patients receive comprehensive care to alleviate pain, promote healing, and prevent recurrence. If you suspect you have an ingrown toenail or are experiencing foot discomfort, seeking prompt attention from a podiatrist is essential for optimal outcomes.




